Introduction
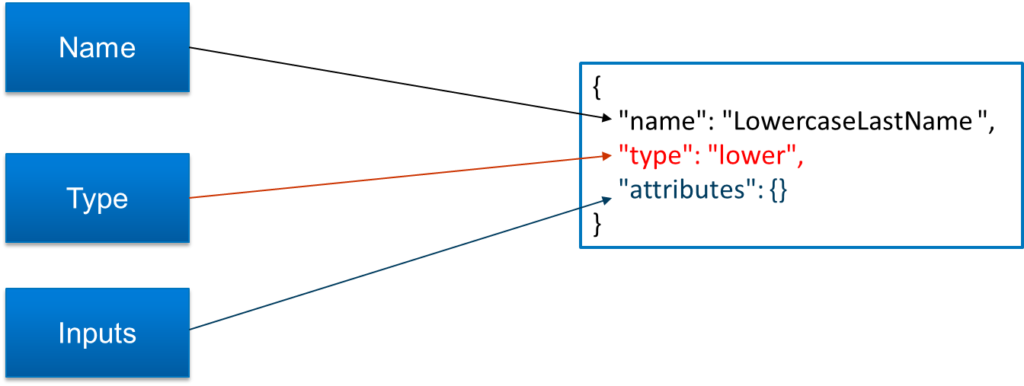
SailPoint Identity Security Cloud Transforms are configurable objects that allow us to manipulate attribute data while aggregating from or provisioning to a source. Sometimes transforms are referred to as Seaspray, the codename for transforms. Identity Security Cloud Transforms and Seaspray are essentially the same.

As we can see from the below diagram, we will be providing input to transform, transformation occurs and output will be returned. So, the way transformation occurs depends on the type of operation used. Some of the transform operations are Concatenation, Conditional, Date Format etc.

Transform REST APIs
In order to create the transform, get transform details, update transform or delete any tranform, we can make use of REST APIs available for transforms.
There are 5 REST APIs are available for transforms in V3 and Beta APIs.
| Rest APIs | Description |
| List Transforms | List Transform API is used to get list of all available transforms from the tenant |
| Create Transform | Create Transform API is used to create a new transform and upload it into the tenant. |
| Transform by ID | Transform by ID is used to get the details of a particular transform. |
| Update Transform | Update a transform API is used to update any existing transform. |
| Delete Transform | Delete transform API is used to delete any transform using transform ID. |
Transform Operations:
In order to make use of transform according to the use case, we should understand various transform operations that are available.
Below are the various types of operations that are available in transform. Each of these operations performs specific task, we can use them according to our needs.
| Transform Operation | Description |
| Account Attribute Transform | Account attribute transform used to look up an account for a particular source on an identity and return a specific attribute value from that account. |
| Base64 Decode Transform | The base64 decode transform allows you to take incoming data that has been encoded using a Base64-based text encoding scheme and render the data in its original binary format. |
| Base64 Encode Transform | Base64 transform will take an input, this input is given to base64 encode transform and the encodes string is returned as output. |
| Decompose Diacritical Marks Transform | Decompose diacritical marks transform to clean or standardize symbols used within language to inform the reader how to say or pronounce a letter. |
| E.164 Phone Transform | Use the E.164 phone transform to convert an incoming phone number string into an E.164-compatible number. |
| Identity Attribute Transform | Transform is used to get the users identity attribute value. |
| Lower Transform | This transform is used to convert input string into lowercase character. |
| Upper Transform | This transform is used to convert input string into uppercase characters. |
In below series of 4 videos, we comprehensively cover all the details around the transforms including basic syntax of transforms, APIs around transforms and all the types of transforms.
Transforms Series – Video 1 of 4:
Below video is the first video in a series of 4 videos about transforms. This part contains an introduction to transforms, syntax of transform, types of Inputs, REST APIs and API Responses.
Video:
Transforms Series – Video 2 of 4: Below video is the second video in a series of 4 videos about transforms. This part contains use cases, transform operations like account attribute transform, base64 decode transform, base64 encode transform, concatenation, conditional, date format, date math, date compare, decompose diacritical marks, first valid, generate random string
Video:
Transforms Series – Video 3 of 4:
Below video is the third video in a series of 4 videos about transforms. This part contains about transform operations like get end of string, get reference identity attribute, identity attribute, index of , ISO3166, last index of, left pad, look up lower, name normalizer, random alphanumeric, random numeric
Video:
Transforms Series– Video 4 of 4:
Below video is the fourth video in a series of 4 videos about transforms. This part contains about transform operations like reference, replace all, replace, right pad, rule, split, static, substring, trim, upper, username generator, UUID generator
Video: