Introduction
API stands for Application Programming Interface. APIs are mechanisms that enable two software components to communicate with each other using a set of definitions and protocols.
API architecture is usually explained in terms of client and server. The application sending the request is called the client and the application sending the response is called the server.
API Workflow
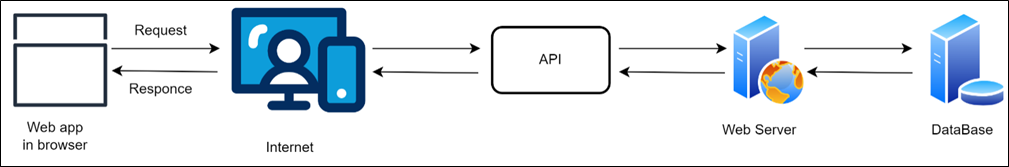
Fig. – API dataflow
What is REST API:
REST stands for Representational State Transfer. This is the most popular and flexible APIs found on the web today. The client sends requests to the server as data. The server uses this client input to start internal functions and returns output data back to the client. REST defines a set of functions like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc. that clients can use to access server data. Clients and servers exchange data using HTTP.
The main feature of REST API is statelessness. Statelessness means that servers do not save client data between requests. Client requests to the server are similar to URLs you type in your browser to visit a website. The response from the server is plain data, without the typical graphical rendering of a web page.
Rest API operation in SailPoint IdentityNow
Post Operation: POST APIs request allows appending data to the endpoint. This is a method used to add information within the request body in the server. It is commonly used for passing delicate information.
GET operations: GET APIs request is used to obtain details from the endpoint and does not have any impact on the endpoint. The GET request does not update any endpoint data while it is triggered.
UPDATE operations: PUT APIs request is used to pass data to the server for creation or modification of an endpoint. The difference between POST and PUT is that POST request is not idempotent.
DELETE operations: DELETE APIs request deletes a resource already present in the server. The DELETE method sends a request to the server for deleting the request mentioned in the endpoint.
Let us understand usage of REST API’s in SailPoint IdentityNow in the following below presentation:
Pre-requisite
- Base URL of SailPoint tenant.
- secret key and client ID for the token generation.
- Generating access token with Authorization code.
Rest API Authentication in IdentityNow
Authentication is the process of determining whether someone or something is, in fact, who or what it says it is. Authentication provides access control for systems by checking to see if a user’s credentials match the credentials in a database of authorized users or in a data authentication server. In doing this, authentication assures secure systems, secure processes and enterprise information security.
OAuth 2.0
- OAuth 2.0 is the industry-standard protocol for AUTHORIZATION.
- OAuth 2.0 is designed primarily as a means of granting access to a set of resources, in simple way OAuth 2.0 Access Token is a string that the OAuth client uses to make requests to the resource server.
JSON Web Token
JSON Web Token (JWT) authentication is a stateless method of securely transmitting information between two parties as (JSON) object. It is often used to authenticate and authorize users in web applications and APIs.
Rest API Authorization in IdentityNow
Authorization in system security is the process of giving the user permission to access a specific resource or Authorization is the act of validating the user’s permission to access a given resource. This term is often used interchangeably with access control or client privilege.
Personal Access Token in IdentityNow
In IdentityNow a personal access token (PAT) is a method of authenticating to an API as a user without providing a username and password.
Now, let us go through a demo on how we can use these REST API’s in SailPoint IdentityNow.
Features of Rest API in IdentityNow
- APIs extend IdentityNow functionality and Usability
- Advanced configuration such as
- Transform creation
- Customization of account profiles
- Ranking authoritative source priority
- System level changes
- Object management
- Interface with other systems – pull data/initiate processes